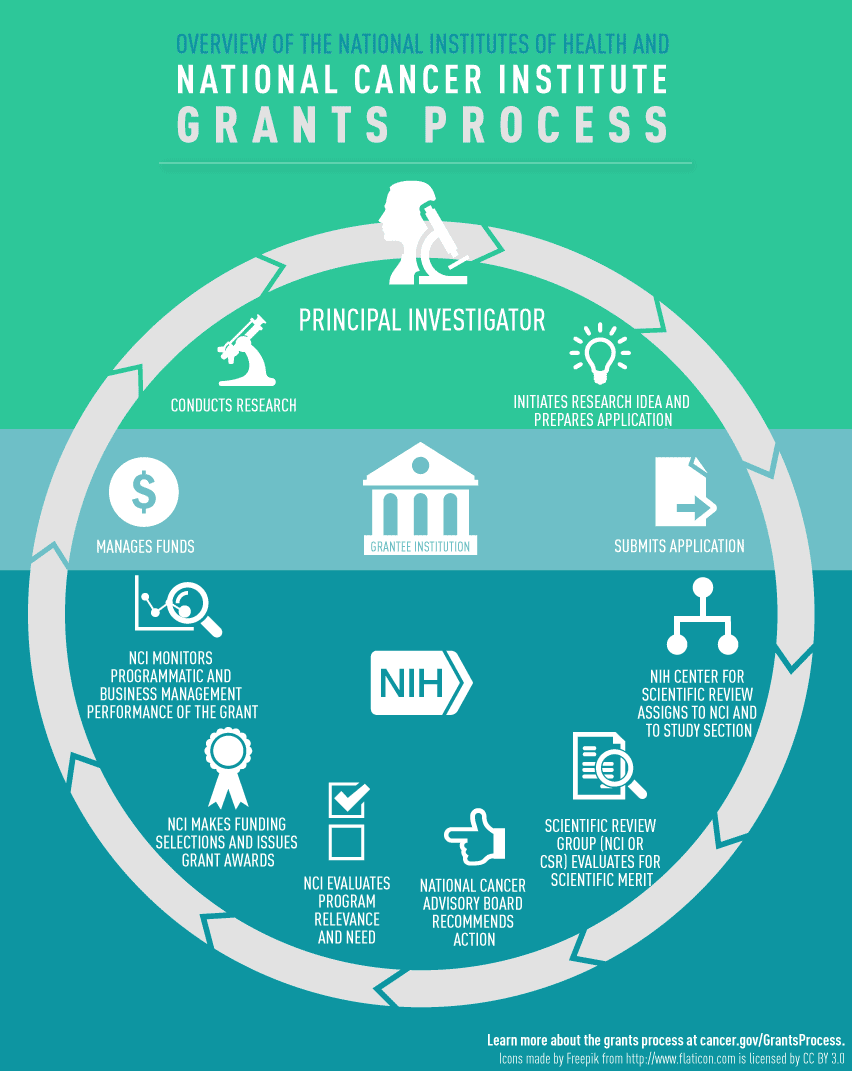
Definition of Roles
There are many individuals and teams involved in the NCI grants process. Learn more about the process in Application Development & Submission.
- Recipient: An organization or individual awarded a grant or cooperative agreement by the NCI that assumes legal, financial, and scientific responsibility and accountability for both the awarded funds and the performance of the grant- supported activity. Also known as awardee or grantee.
- Recipient Institution/Organization: Legally responsible and accountable to the NCI for the performance and financial aspects of the grant-supported activity.
- Institutional Business Official (BO): Person working in a research organization’s business office who has signature or other authority. That person is the same as the Grants.gov Authorized Organizational Representative (AOR) and the eRA Commons Signing Official (SO).
- Principal Investigator (PI): Individual designated by the recipient organization to direct the project or activity being supported by the grant and is responsible and accountable to recipient organization officials for the proper conduct of the project or program.
- NCI Program Directors/Program Officers: Individual responsible for the programmatic, scientific and/or technical oversight of a grant portfolio. This individual collaborates closely with Grants Management Specialists to provide oversight of the NCI grants program.
- NCI Grants Management Officer (GMO): Individual responsible for all business management aspects of grants and cooperative agreements, including review, negotiation, award, and administration.
- Grants Management Specialist: Individual selected by the GMO to oversee the business and other non-programmatic aspects of a portfolio of grants and cooperative agreements.
- Institute/Center (IC): The NIH organizational component responsible for a particular grant program or set of activities. The NCI is an IC.
Funding Types
The NCI supports cancer research that spans the continuum from basic science to clinical research to research on implementation, cancer control, and cancer care delivery through an extramural program of grants, cooperative agreements, and research and development contracts.
- Grant: Provides federal financial assistance including money, property, or both to an eligible entity to perform approved scientific activities with little or no government involvement.
- Cooperative Agreement: A support mechanism where the NCI and extramural scientists/clinicians work together during performance of the research.
- Research and Development (R&D) Contract: Used to obtain or procure cancer research services and other resources needed by the federal government.
Solicitation & Application Types
The NCI uses these solicitation types to encourage grant application submissions through the publication of Notices of Funding Opportunities (NOFOs):
- Program Announcement (PA): A formal statement about a new or ongoing extramural activity or program
- Requests for Applications (RFAs): Issued to invite grant applications in a well-defined scientific area to accomplish specific IC program objectives
There are nine grant application types that may be used to identify the stages in the lifecycle of a grant. The grant type defines the procedures and specifies the documents required to process the grant award.
- Type 1: New
- Type 2: Renewal (a.k.a. Competing Continuation)
- Type 3: Competing Revision /Administrative Supplement
- Type 4: Extension
- Type 5: Noncompeting Continuation
- Type 6: Successor-in-Interest and Name-Change Agreements
- Type 7: Change of Institution
- Type 8: Change of NIH awarding Institute or Center (for Type 5)
- Type 9: Change of NIH awarding Institute or Center (for Type 2)
Learn more in Application Development and Submission.
Allowable Costs
Research grant funds are awarded to supplement or complement the support of research at an institution. Grant funds may be used for:
- Allowable direct costs specifically incurred in the conduct of the research project
- Facilities and administrative (F&A) costs (formerly known as indirect costs or overhead) resulting from an institution providing support services
Learn more about determining your budget in Application Development and Submission.
Apply for a Grant
The NCI grants process begins with developing and submitting your application. NCI and NIH offer guidance and resources to help.
NCI Resources
Visit NCI’s Apply for a Grant section for NCI-specific instructions.
NIH Resources
- How to Plan Your Application
- How to Write Your Application
- How to Develop Your Budget
- How to Apply
- How to Track Your Application
Grant Document Examples
- Grant Application Face Page
- Summary Statement (via NIAID)
Notice of Award (NoA)
During the application process, each application undergoes an extensive review. When a grant is funded, the NIH will issue a Notice of Award. An NOA is the official, legally binding document, signed (or the electronic equivalent of signature) by a Grants Management Officer that:
- notifies the recipient of the award of a grant;
- contains or references all the terms and conditions of the grant and Federal funding limits and obligations; and,
- provides the documentary basis for recording the obligation of Federal funds in the NIH accounting system
Manage Your Award
There are many requirements that recipient organizations need to be aware of to ensure they are successful stewards of federal funds.
For a more information about management requirements, visit NCI’s Manage Your Award section: