Cancer and Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology, which involves controlling matter at the tiniest scale, is capable of creating unique structures and devices which find use in cancer research and oncology. These structures, in combination with molecular discoveries, can provide tools needed to develop advanced diagnostics, treatments, and preventive measures for cancer.
Nanotechnology is about working with materials and structures at an incredibly small scale, ranging from about 1 to 100 nanometers as defined by the U.S. National Nanotechnology Initiative (NNI). At this level, matter behaves in special ways that can be harnessed for specific purposes. These tiny structures can be used on their own or integrated into larger systems, offering great possibilities in cancer research and healthcare.
Nanotechnology has the potential to significantly improve cancer diagnosis and treatment. Although scientists and engineers started exploring these technologies only in the 1980s, there has been significant progress in using nano-based therapies and diagnostics in the clinic, with many more interventions in development.
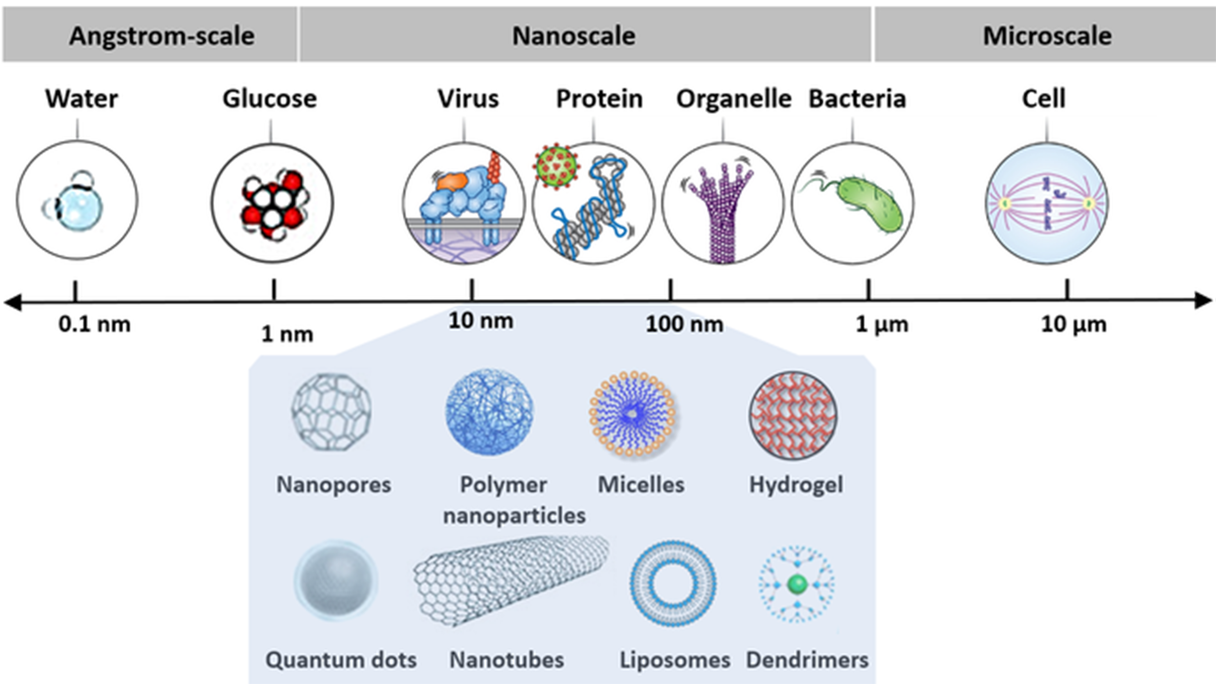
Nanoscale devices are incredibly tiny, ranging in size from one hundred to ten thousand times smaller than human cells. The depiction displays this scale in size. Adapted from Yicong Wu and Hari Shroff, Histochemistry and Cell Biology, 2022.
Credit: National Cancer Institute
This emerging and exciting field unites scientists from diverse disciplines, including physicists, chemists, engineers, information technologists, computer scientists, mathematicians, material scientists, and biologists. Nanotechnology finds applications in nearly every area of life, such as electronics, magnetics, optics, information technology, materials development, and biomedicine. Already, nanotechnology-based structures and devices are fueling numerous innovative applications in various fields, including the realm of medicine.
-
Benefits of Nanotechnology for Cancer
Nanotechnology offers many possible benefits to early detection, diagnosis, and therapy of cancer. These benefits are enabled by combining small size and unique properties of nanoparticles and nano-devices with biological discoveries to overcome some of the challenges of contemporary medicine.
-

Early Detection and Diagnosis
In the struggle against cancer, half of the battle is won through its early detection and reliable diagnosis of the disease. Furthermore, tools that enable precise monitoring of patient response to therapy can optimize treatment and improve patient outcomes. Find out how nanotechnology can improve diagnosis of cancer.
-
Treatment and Therapy
Nanotechnology offers means to precisely administer therapies to cancerous cells and tissues. With these tools, clinicians can effectively deliver chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and the next generation of immuno- and gene therapies directly to the tumor in a safer way. Additionally, nanotechnology tools can guide and improve surgical resection of tumors. Find out how nanotechnology can improve cancer treatment.
-
Cancer Nano-therapies in the Clinic and in Clinical Trials
Nanotechnology-based cancer interventions have been in the development for some time and several of them are already in clinical use benefiting the patients. Find a list of currently approved nano-enabled therapeutics and those in clinical trials.
-

Safety of Nanotechnology Cancer Treatments
Nanotechnology is a potent approach for improving diagnosis and treatment of cancer. A complete understanding and safe use of nanotechnologies in cancer is crucial to fully unlock its potential in medicine and oncology.