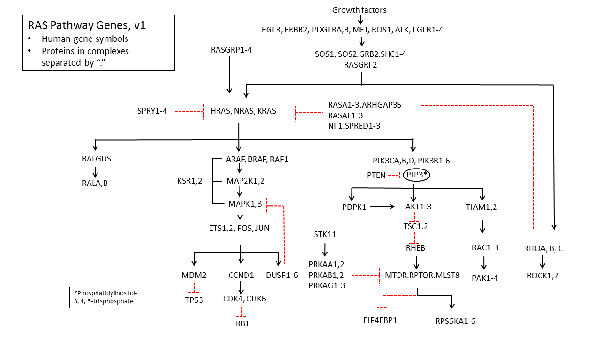
What Do We Mean By "RAS Pathway"?
, by Frank McCormick
Dear all,
We are planning a paper that presents a RAS-centric view of the data in TCGA. This will be a collaboration between Gaddy Getz and colleagues at the Broad, and Bob Stephens and colleagues at the Frederick National Lab and others. The aim is to provide a synopsis of expression patterns, mutations and copy number changes, and several other parameters relevant to the RAS pathway across the different tumor types.
As you all know, this pathway can be defined in various ways. For purposes of interrogating TCGA data we have used gene names from the Broad Tumor Portal. Some may not be familiar to you. For example, I hadn’t realized that ARHGAP35, which is mutated at quite a high frequency, is actually p190RhoGAP, made popular by Jeff Settleman. Matt Meyerson kindly pointed this out to me.
Anyway, we'd be very grateful if you could send suggestions for genes that we missed or errors in the pathway diagram. Any other suggestions for making this effort more useful would be welcome, particularly in the context of how to best share the TCGA data in the most useful way possible.
Provide your feedback by commenting below or email me at SolveRAS@nih.gov.
Cheers,
Frank
Gene Names, Cognate Proteins, and Aliases in the RAS Pathway
The table comprises the name of each human gene in the RAS Pathway diagram, the name of the cognate protein for each gene, and gene aliases (alternative names). The aliases in bold are gene names more commonly used by RAS researchers.
| Gene name | Protein name from Uniprot or BioGPS | Alternative gene names from BioGPS |
|---|---|---|
| AKT1 | RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase | AKT, CWS6, PKB, PKB-ALPHA, PRKBA, RAC, RAC-ALPHA |
| AKT2 | RAC-beta serine/threonine-protein kinase | HIHGHH, PKBB, PKBBETA, PRKBB, RAC-BETA |
| AKT3 | RAC-gamma serine/threonine-protein kinase | MPPH, MPPH2, PKB-GAMMA, PKBG, PRKBG, RAC-PK-gamma, RAC-gamma, STK-2 |
| ALK | Anaplastic lymphoma receptor tyrosine kinase; ALK tyrosine kinase receptor | CD246, NBLST3 |
| ARAF | Serine/threonine-protein kinase A-Raf | A-RAF, ARAF1, PKS2, RAFA1 |
| ARHGAP35 | Rho GTPase-activating protein 35 | GRF-1, GRLF1, P190-A, P190A, p190ARhoGAP, p190RhoGAP |
| BRAF | Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf | B-RAF1, BRAF1, NS7, RAFB1 |
| CCND1 | Cyclin D1 | BCL1, D11S287E, PRAD1, U21B31 |
| CDK4 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 | CMM3, PSK-J3 |
| CDK6 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 | PLSTIRE |
| DUSP1 | Dual specificity phosphatase 1 | CL100, HVH1, MKP-1, MKP1, PTPN10 |
| DUSP2 | Dual specificity phosphatase 2 | PAC-1, PAC1 |
| DUSP3 | Dual specificity phosphatase 3 | VHR |
| DUSP4 | Dual specificity phosphatase 4 | HVH2, MKP-2, MKP2, TYP |
| DUSP5 | Dual specificity phosphatase 5 | DUSP, HVH3 |
| DUSP6 | Dual specificity phosphatase 6 | HH19, MKP3, PYST1 |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor | ERBB, ERBB1, HER1, PIG61, mENA |
| EIF4EBP1 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1 | 4E-BP1, 4EBP1, BP-1, PHAS-I |
| ERBB2 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 | CD340, HER-2, HER-2/neu, HER2, MLN 19, NEU, NGL, TKR1 |
| ETS1 | v-ets avian erythroblastosis virus E26 oncogene homolog 1 | ETS-1, EWSR2, p54 |
| ETS2 | v-ets avian erythroblastosis virus E26 oncogene homolog 2 | ETS2IT1 |
| FGFR1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | BFGFR, CD331, CEK, FGFBR, FGFR-1, FLG, FLT-2, FLT2, HBGFR, HH2, HRTFDS, KAL2, N-SAM, OGD, bFGF-R-1 |
| FGFR2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | BBDS, BEK, BFR-1, CD332, CEK3, CFD1, ECT1, JWS, K-SAM, KGFR, TK14, TK25 |
| FGFR3 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 | CH, CD333, CEK2, HSFGFR3EX, JTK4 |
| FGFR4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | CD334, JTK2, TKF |
| FOS | FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog | AP-1, C-FOS, p55 |
| GRB2 | Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 | ASH, EGFRBP-GRB2, Grb3-3, MST084, MSTP084, NCKAP2 |
| HRAS | GTPase HRas | C-BAS/HAS, C-H-RAS, C-HA-RAS1, CTLO, H-RASIDX, HAMSV, HRAS1, RASH1, p21ras |
| JUN | Jun proto-oncogene | AP-1, AP1, c-Jun |
| KRAS | GTPase KRas | C-K-RAS, CFC2, K-RAS2A, K-RAS2B, K-RAS4A, K-RAS4B, KI-RAS, KRAS1, KRAS2, NS, NS3, RASK2 |
| KSR1 | Kinase suppressor of Ras 1 | KSR, RSU2 |
| KSR2 | Kinase suppressor of Ras 2 | [none] |
| MAP2K1 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 | CFC3, MAPKK1, MEK1, MKK1, PRKMK1 |
| MAP2K2 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 | CFC4, MAPKK2, MEK2, MKK2, PRKMK2 |
| MAPK1 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 | ERK, ERK-2, ERK2, ERT1, MAPK2, P42MAPK, PRKM1, PRKM2, p38, p40, p41, p41mapk, p42-MAPK |
| MAPK3 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 | ERK-1, ERK1, ERT2, HS44KDAP, HUMKER1A, P44ERK1, P44MAPK, PRKM3, p44-ERK1, p44-MAPK |
| MDM2 | MDM2 proto-oncogene, E3 ubiquitin protein ligase | ACTFS, HDMX, hdm2 |
| MET | MET proto-oncogene, receptor tyrosine kinase; hepatocyte growth factor receptor | AUTS9, HGFR, RCCP2, c-Met |
| MLST8 | MTOR associated protein, LST8 homolog (S. cerevisiae) | GBL, GbetaL, LST8, POP3, WAT1 |
| MTOR | Mechanistic target of rapamycin (serine/threonine kinase) | FRAP, FRAP1, FRAP2, RAFT1, RAPT1 |
| NF1 | Neurofibromin | NFNS, VRNF, WSS |
| NRAS | GTPase NRas | ALPS4, CMNS, N-ras, NCMS, NRAS1, NS6 |
| PAK1 | p21 protein (Cdc42/Rac)-activated kinase 1 | PAKalpha |
| PAK2 | p21 protein (Cdc42/Rac)-activated kinase 2 | PAK65, PAKgamma |
| PAK3 | p21 protein (Cdc42/Rac)-activated kinase 3 | CDKN1A, MRX30, MRX47, OPHN3, PAK3beta, bPAK, hPAK3 |
| PAK4 | p21 protein (Cdc42/Rac)-activated kinase 4 | [none] |
| PDGFRA | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | CD140A, PDGFR-2, PDGFR2, RHEPDGFRA |
| PDGFRB | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta | CD140B, IBGC4, IMF1, JTK12, PDGFR, PDGFR-1, PDGFR1 |
| PDPK1 | 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 | PDK1, PDPK2, PRO0461 |
| PIK3CA | Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha isoform | CLOVE, CWS5, MCAP, MCM, MCMTC, PI3K, p110-alpha |
| PIK3CB | Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit beta isoform | P110BETA, PI3K, PI3KBETA, PIK3C1 |
| PIK3CD | phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase, catalytic subunit delta | APDS, IMD14, P110DELTA, PI3K, p110D |
| PIK3R1 | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit alpha | AGM7, GRB1, p85, p85-ALPHA |
| PIK3R2 | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit beta | MPPH, MPPH1, P85B, p85, p85-BETA |
| PIK3R3 | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit gamma | p55, p55-GAMMA |
| PIK3R4 | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase regulatory subunit 4 | VPS15, p150 |
| PIK3R5 | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase regulatory subunit 5 | F730038I15Rik, FOAP-2, P101-PI3K, p101 |
| PIK3R6 | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase regulatory subunit 6 | C17orf38, HsT41028, p84 PIKAP, p87(PIKAP), p87PIKAP |
| PRKAA1 | 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-1 | AMPK, AMPKa1 |
| PRKAA2 | 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-2 | AMPK, AMPK2, AMPKa2, PRKAA |
| PRKAB1 | 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase subunit beta-1 | AMPK, HAMPKb |
| PRKAB2 | 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase subunit beta-2 | [none] |
| PRKAG1 | Protein kinase, AMP-activated, gamma 1 non-catalytic subunit | AMPKG |
| PRKAG2 | Protein kinase, AMP-activated, gamma 2 non-catalytic subunit | AAKG, AAKG2, CMH6, H91620p, WPWS |
| PRKAG3 | Protein kinase, AMP-activated, gamma 3 non-catalytic subunit | AMPKG3 |
| PTEN | Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate 3-phosphatase and dual-specificity protein phosphatase PTEN | 10q23del, BZS, CWS1, DEC, GLM2, MHAM, MMAC1, PTEN1, TEP1 |
| RAC1 | Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (rho family, small GTP binding protein Rac1) | Rac-1, TC-25, p21-Rac1 |
| RAC2 | Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 2 (rho family, small GTP binding protein Rac2) | EN-7, Gx, HSPC022, p21-Rac2 |
| RAC3 | Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 3 (rho family, small GTP binding protein Rac3) | [none] |
| RAF1 | RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase | CMD1NN, CRAF, NS5, Raf-1, c-Raf |
| RALA | Ras-related protein Ral-A | RAL |
| RALB | Ras-related protein Ral-B | [none] |
| RALGDS | Ral guanine nucleotide dissociation stimulator | RGDS, RGF, RalGEF |
| RASA1 | Ras GTPase-activating protein 1 | CM-AVM, CMAVM, GAP, PKWS, RASA, RASGAP, p120GAP, p120RASGAP |
| RASA2 | Ras GTPase-activating protein 2 | GAP1M |
| RASA3 | Ras GTPase-activating protein 3 | GAP1IP4BP, GAPIII |
| RASAL1 | RasGAP-activating-like protein 1 | RASAL |
| RASAL2 | Ras GTPase-activating protein nGAP | NGAP |
| RASAL3 | RAS protein activator like-3 | [none] |
| RASGRF2 | Ras-specific guanine nucleotide-releasing factor 2 | GRF2, RAS-GRF2 |
| RASGRP1 | RAS guanyl-releasing protein 1 | CALDAG-GEFI, CALDAG-GEFII, RASGRP, V, hRasGRP1 |
| RASGRP2 | RAS guanyl-releasing protein 2 | CALDAG-GEFI, CDC25L |
| RASGRP3 | Ras guanyl-releasing protein 3 | GRP3, KIAA0846 |
| RASGRP4 | RAS guanyl-releasing protein 4 | [none] |
| RB1 | Retinoblastoma 1 | OSRC, PPP1R130, RB, p105-Rb, pRb, pp110 |
| RHEB | Ras Homolog Enriched In Brain, GTP-binding protein Rheb | RHEB2 |
| RHOA | Ras homolog family member A | ARH12, ARHA, RHO12, RHOH12 |
| RHOB | Ras homolog family member B | ARH6, ARHB, MST081, MSTP081, RHOH6 |
| RHOC | Ras homolog family member C | ARH9, ARHC, H9, RHOH9 |
| ROCK1 | Rho-associated, coiled-coil containing protein kinase 1 | P160ROCK, ROCK-I |
| ROCK2 | Rho-associated, coiled-coil containing protein kinase 2 | ROCK-II |
| ROS1 | ROS proto-oncogene 1 , receptor tyrosine kinase | MCF3, ROS, c-ros-1 |
| RPS6KA1 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-1 | MAPKAPK1A, RSK1 |
| RPS6KA2 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-2 | HU-2, MAPKAPK1C, RSK, RSK3, S6K-alpha, S6K-alpha2, p90-RSK3, pp90RSK3 |
| RPS6KA3 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-3 | CLS, HU-3, ISPK-1, MAPKAPK1B, MRX19, RSK, RSK2, S6K-alpha3, p90-RSK2, pp90RSK2 |
| RPS6KA4 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-4 | MSK2, RSK-B |
| RPS6KA5 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-5 | MSK1, MSPK1, RLPK |
| RPS6KA6 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-6 | PP90RSK4, RSK4 |
| RPTOR | Regulatory associated protein of MTOR, complex 1 | KOG1, Mip1 |
| SHC1 | SHC (Src homology 2 domain containing) transforming protein 1 | SHC, SHCA |
| SHC2 | SHC (Src homology 2 domain containing) transforming protein 2 | SCK, SHCB, SLI |
| SHC3 | SHC (Src homology 2 domain containing) transforming protein 3 | N-Shc, NSHC, RAI, SHCC |
| SHC4 | SHC (Src homology 2 domain containing) transforming protein 4 | RaLP, SHCD |
| SOS1 | Son of sevenless homolog 1 | GF1, GGF1, GINGF, HGF, NS4 |
| SOS2 | Son of sevenless homolog 2 | [none] |
| SPRED1 | Sprouty-related, EVH1 domain-containing protein 1 | NFLS, PPP1R147, hSpred1, spred-1 |
| SPRED2 | Sprouty-related, EVH1 domain-containing protein 2 | Spred-2 |
| SPRED3 | Sprouty-related, EVH1 domain-containing protein 3 | Eve-3, spred-3 |
| SPRY1 | Protein sprouty homolog 1 | hSPRY1 |
| SPRY2 | Protein sprouty homolog 2 | hSPRY2 |
| SPRY3 | Protein sprouty homolog 3 | HSPRY3, spry-3 |
| SPRY4 | Protein sprouty homolog 4 | HH17 |
| STK11 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STK11 | LKB1, PJS, hLKB1 |
| TIAM1 | T-lymphoma invasion and metastasis-inducing protein 1 | [none] |
| TIAM2 | T-lymphoma invasion and metastasis-inducing protein 2 | STEF, TIAM-2 |
| TP53 | tumor protein p53 | BCC7, LFS1, P53, TRP53 |
| TSC1 | Tuberous Sclerosis 1, Hamartin | LAM, TSC |
| TSC2 | Tuberous Sclerosis 2, Tuberin | LAM, PPP1R160, TSC4 |