axicabtagene ciloleucel
(AK-see-KAB-tuh-jeen sy-loh-LOO-sel)
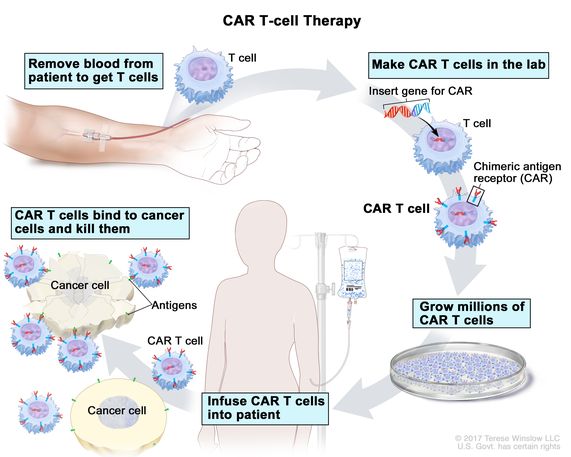
A drug used to treat adults with follicular lymphoma or certain types of large B-cell lymphoma that relapsed (came back) or did not get better after treatment with at least two other types of systemic therapy. It is also being studied in the treatment of other types of cancer. Axicabtagene ciloleucel is made using a patient’s T cells (a type of immune system cell). A gene for a special receptor called chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) is added to the T cells in the laboratory. These changed T cells called CAR T cells are grown in large numbers in the laboratory and given to the patient by infusion. Axicabtagene ciloleucel binds to a protein called CD19, which is found on most B-cell lymphoma cells. This helps the body’s immune system kill cancer cells. Axicabtagene ciloleucel is a type of CAR T-cell therapy. Also called Yescarta.