deoxyribonucleic acid
(dee-OK-see-RY-boh-noo-KLAY-ik A-sid)
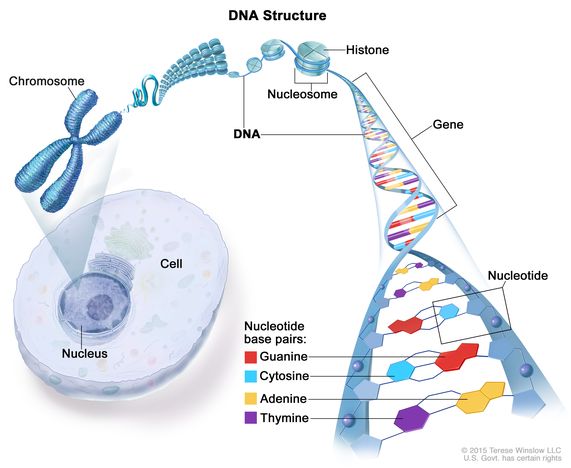
The molecule inside cells that contains the genetic information needed for a person and most other organisms to develop and grow and is passed from one generation to the next. Deoxyribonucleic acid is made up of two strands that twist into the shape of a spiral ladder called a double helix. Each strand has a backbone that is made up of sugar and phosphate molecules that attach to one of four bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). The bases pair up with one another (A with T, and G with C) to form chemical bonds, which act like rungs on a ladder. This holds the two strands of deoxyribonucleic acid together. Also called DNA.