keratinocyte carcinoma
(KAYR-uh-TIH-noh-site KAR-sih-NOH-muh)
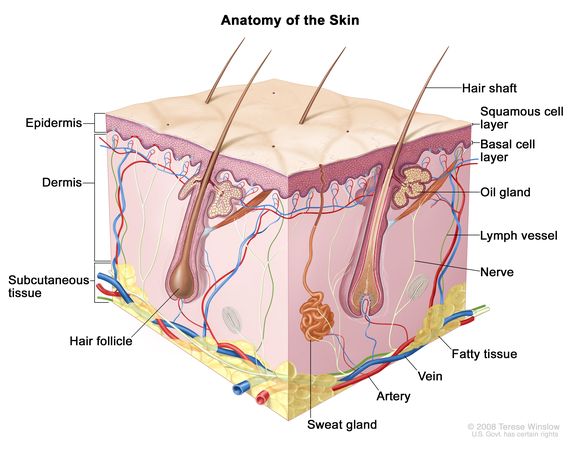
Cancer that forms in the tissues of the epidermis (the outer layer of the skin). The two main types of keratinocyte carcinoma are squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), which begins in thin, flat cells that form the top layer of the epidermis, and basal cell carcinoma (BCC), which begins in round cells that form the lower layer of the epidermis. SCC and BCC are the most common types of skin cancer. Keratinocyte carcinoma can occur anywhere on the body, but it is most common in areas of the skin often exposed to sunlight, such as the face, ears, lower lip, neck, arms, and top of the hands. Also called nonmelanoma skin cancer.