multiple endocrine adenomatosis type 2
(MUL-tih-pul EN-doh-krin A-deh-NOH-muh-TOH-sis ...)
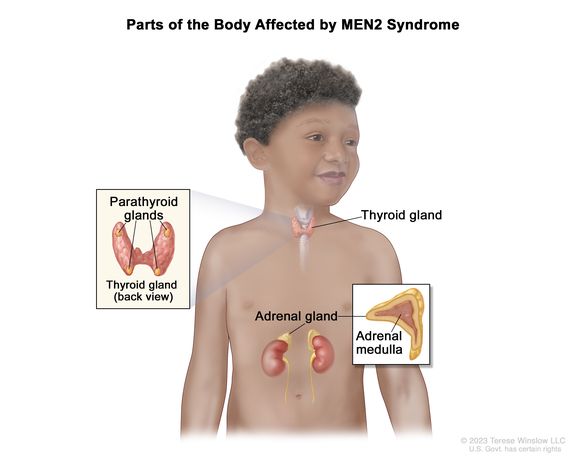
A rare, genetic disorder that affects the endocrine glands and can cause tumors in the thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, and adrenal glands. The affected endocrine glands may make high levels of hormones, which can lead to other medical problems such as high blood pressure and kidney stones. Multiple endocrine adenomatosis type 2 is caused by a mutation (change) in a gene called RET, and is divided into three subtypes (MEN2A, MEN2B, and FMTC). People with all subtypes of multiple endocrine adenomatosis type 2 have an increased risk of medullary thyroid cancer, pheochromocytoma, and parathyroid gland cancer. Also called MEN2, MEN2 syndrome, and multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 syndrome.