nuclear magnetic resonance imaging
(NOO-klee-er mag-NEH-tik REH-zuh-nunts IH-muh-jing)
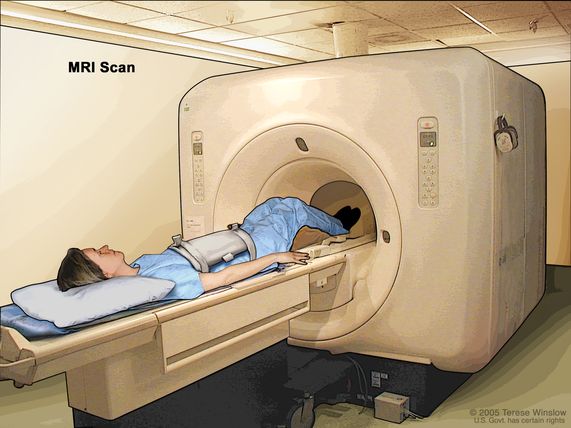
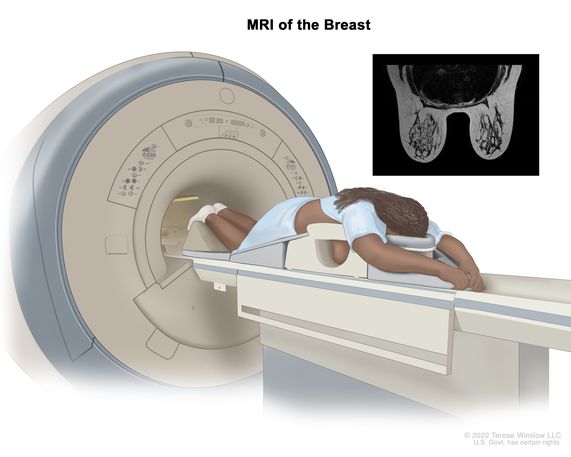
A procedure that uses radio waves, a powerful magnet, and a computer to make a series of detailed pictures of areas inside the body. A contrast agent, such as gadolinium, may be injected into a vein to help the tissues and organs show up more clearly in the picture. Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging may be used to help diagnose disease, plan treatment, or find out how well treatment is working. It is especially useful for imaging the brain and spinal cord, the heart and blood vessels, the bones, joints, and other soft tissues, the organs in the pelvis and abdomen, and the breast. Also called magnetic resonance imaging, MRI, and NMRI.