Cockayne syndrome
(KAH-kayn SIN-drome)
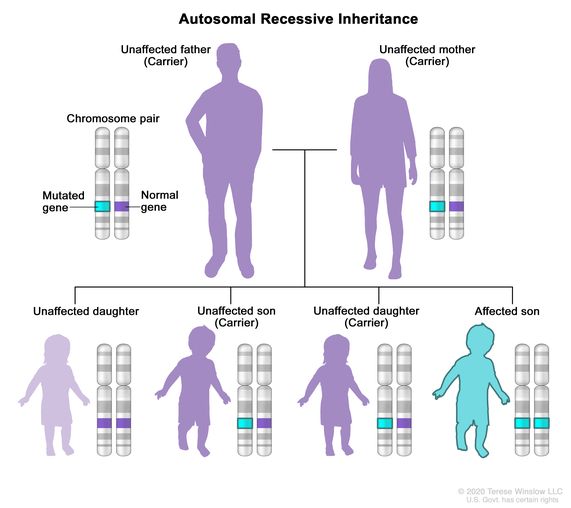
A rare genetic disorder that is caused by inheriting two mutations (changes) in the ERCC6 gene or in the ERCC8 gene. These genes make proteins involved in DNA repair. Cockayne syndrome is marked by shorter-than-average height, an abnormally small head, premature aging, sensitivity to light, and learning and developmental delays. Other signs and symptoms may include hearing loss, vision problems, tooth decay, bone abnormalities, and nervous system problems. The signs and symptoms usually appear during infancy and get worse over time. Cockayne syndrome is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner.