March 2023 - Cancer Currents Blog
-
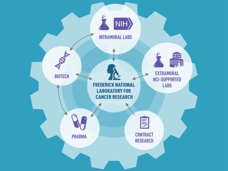
Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research: A Unique Resource for the Biomedical Research Community
To mark the 10 years since it was named a national lab, NCI Principal Deputy Director Douglas R. Lowy, M.D., discusses some of the Frederick National Lab’s initiatives to support cancer research and looks ahead at the next 10 years.
-
New on NCI’s Websites for March 2023
NCI periodically provides updates on new websites and other online content of interest to the cancer community. See selected content that has been added as of March 2023.
-
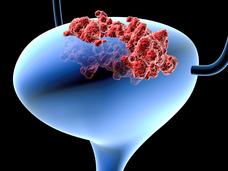
Immunotherapy after Surgery Shows Long-Term Benefits for High-Risk Bladder Cancer
Updated results from a large clinical trial confirm that, for some people with bladder cancer, receiving immunotherapy after surgery is an effective treatment. In 2021, initial results from the same trial led to FDA approval of nivolumab (Opdivo) for this use.
-
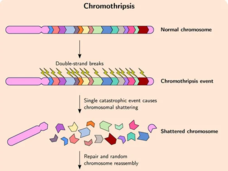
Strategy May Prevent Tumor Resistance to Targeted Cancer Therapies
Researchers have identified a mechanism by which cancer cells develop specific genetic changes needed to become resistant to targeted therapies. They also showed that this process, called non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ), can potentially be disrupted.
-
Dexrazoxane Protects the Heart Long Term for Kids Being Treated for Cancer
Doxorubicin is used to treat many types of childhood cancer, but it can damage the heart. Giving dexrazoxane (Zinecard) before each dose substantially decreases a child’s risk of treatment-related heart problems in adulthood, new study results show.
-
Lung-Sparing Surgery Is Effective for Some with Early-Stage Lung Cancer
For certain people with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer, sublobar surgery to remove only a piece of the affected lung lobe is as effective as surgery to remove the whole lobe, new research shows.
-
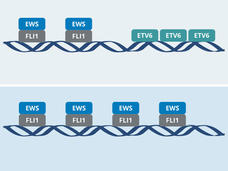
ETV6 Protein Could Be an Important Target for Ewing Sarcoma Treatment
The protein ETV6 appears to promote tumor growth by affecting the behavior of the EWS-FLI1 fusion protein that drives most Ewing sarcomas. The research groups that made the discovery hope it leads to a targeted therapy for the aggressive childhood cancer.