August 2017 - Cancer Currents Blog
-
Bringing the Investigational Breast Cancer Drug Endoxifen from Bench to Bedside with NCI Support
Researchers recognized the potential of endoxifen as a treatment for breast cancer and, with NCI support, developed the compound into a drug now being tested in clinical trials.
-
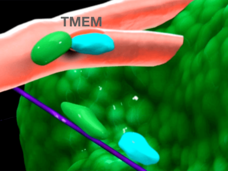
Modified Stem Cells Deliver Chemotherapy to Metastatic Tumors
Researchers have used modified stem cells to deliver a cancer drug selectively to metastatic breast cancer tumors in mice. The stem cells target metastatic tumors by homing in on the stiff environment that typically surrounds them.
-
Two New Therapies Approved for Acute Myeloid Leukemia
FDA has approved two new treatments for some adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML): enasidenib (Idhifa®), which targets the IDH2 protein; and liposomal cytarabine-daunorubicin CPX-351 (Vyxeos®), a two-drug chemotherapy combination encapsulated in liposomes.
-
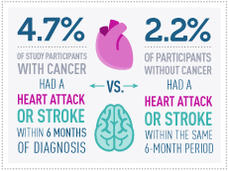
Heart Attack, Stroke Risk May Be Elevated Following Cancer Diagnosis
A diagnosis of cancer can come with an increased risk of a heart attack or stroke in the months after beginning treatment, a new study suggests. Within 6 months of a diagnosis, the risk of either event was more than twice that seen in people without cancer.
-
Neratinib Approved by FDA for HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
FDA has approved neratinib for patients with early-stage HER2-positive breast cancer who have finished at least 1 year of adjuvant therapy with trastuzumab.
-
NCI Program Supports Small Businesses to Advance Cancer Research Innovation – A Q&A with Michael Weingarten
NCI’s Small Business Innovation Research Program recently issued contract solicitations to spur the development of new cancer-related therapies and technologies, including seven opportunities specific to the Cancer Moonshot.
-
FDA Approves Nivolumab for Some Metastatic Colorectal Cancers
FDA has granted accelerated approval to the immunotherapy drug nivolumab (Opdivo®) for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer whose tumors have alterations that affect DNA repair.
-
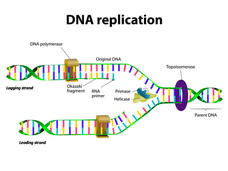
Study Uncovers Previously Unrecognized Effect of Chemotherapy
A new study conducted primarily in mice suggests that chemotherapy given before surgery for breast cancer can cause changes in cells in and around the tumor that are tied to an increased risk of the cancer spreading to other areas of the body.
-
Ibrutinib Becomes First FDA-Approved Drug for Chronic Graft-Versus-Host Disease
A drug used to treat several blood cancers, ibrutinib, has been approved by FDA to treat chronic graft-versus-host disease, making it the first approved therapy for this potentially fatal side effect of cancer-related stem cell transplants.
-
Dual-Biomarker Blood Test Shows Promise for Pancreatic Cancer Early Detection
A new blood test that measures levels of two specific proteins may be able to accurately detect pancreatic cancer at its earliest stages, when it is most likely to respond to treatment, findings from a new study suggest.
-
“First in Human” Documentary Highlights NCI Immunotherapy Research
The Discovery Channel special, First in Human, will feature some of the groundbreaking work on cancer immunotherapy being done at the NIH Clinical Center, including CAR T-cell therapy and TIL therapy.
-
In Melanoma, Personalized Treatment Vaccines Show Promise
Results of an early-phase trial showed that a treatment vaccine personalized to a specific patient’s cancer generated a robust immune response against the cancer and may have helped to prevent it from returning.
-
Glioblastoma—Unraveling the Threads: A Q&A with Drs. Mark Gilbert and Terri Armstrong of the NIH Neuro-Oncology Branch
Progress against the brain cancer glioblastoma has been slow. Drs. Mark Gilbert and Terri Armstrong of NCI’s Neuro-Oncology Branch discuss why and what’s being done to change that.
-
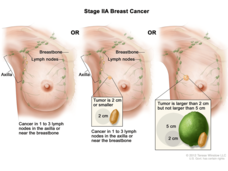
Survivors of Breast Cancer Differ on Who Should Manage Follow-Up Care
Many survivors of early-stage breast cancer prefer that their oncologist handle aspects of routine medical care usually overseen by primary care practitioners, leading to concerns about gaps in care.