Treatment - Cancer Currents Blog
Cancer treatment related news, with context from leading experts. Includes articles on new therapies, treatment side effects, and important trends in treatment-related research.
-
Studies Identify Therapies That May Delay Melanoma Recurrence after Surgery
Two recent clinical trials have identified treatments that may delay cancer from returning in some patients with melanoma. Patients in both trials had advanced melanoma that was surgically removed, and each trial tested different forms of post-surgical, or adjuvant, therapy.
-
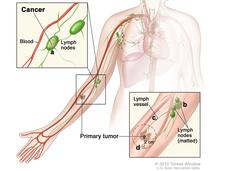
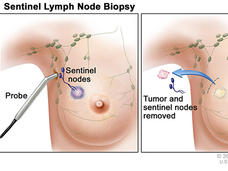
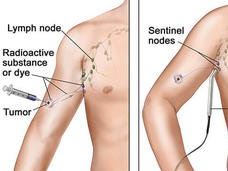
Extensive Lymph Node Removal Doesn't Improve Survival in Some Women with Early-Stage Breast Cancer
Long-term results from a large clinical trial confirm that, for some women with early-stage breast cancer who have lumpectomy as their surgical treatment, a less extensive lymph node biopsy approach is sufficient.
-
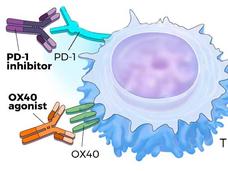
Timing and Sequence Critical for Immunotherapy Combination
When given at the same time, two immune checkpoint inhibitors were ineffective against breast cancer growth in mice, a new study found. The combination was more effective and safer if the two inhibitors were given in a specific sequence.
-
Long-Term Nerve Damage Possible after Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer
Many women who receive taxane-based chemotherapy to treat breast cancer experience long-term nerve damage, or peripheral neuropathy, data from a large clinical trial show.
-
Forgoing Conventional Cancer Treatments for Alternative Medicine Increases Risk of Death
In a large study, patients with nonmetastatic breast, lung, or colorectal cancer who chose alternative therapies had substantially worse survival than patients who received conventional cancer treatments.
-
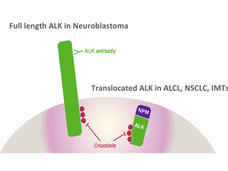
Crizotinib Shows Promise for Childhood Cancers
In a small clinical trial, the drug crizotinib shrank tumors in children with cancers that have alterations in the ALK gene.
-
Bringing the Investigational Breast Cancer Drug Endoxifen from Bench to Bedside with NCI Support
Researchers recognized the potential of endoxifen as a treatment for breast cancer and, with NCI support, developed the compound into a drug now being tested in clinical trials.
-
Modified Stem Cells Deliver Chemotherapy to Metastatic Tumors
Researchers have used modified stem cells to deliver a cancer drug selectively to metastatic breast cancer tumors in mice. The stem cells target metastatic tumors by homing in on the stiff environment that typically surrounds them.
-
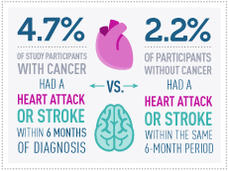
Heart Attack, Stroke Risk May Be Elevated Following Cancer Diagnosis
A diagnosis of cancer can come with an increased risk of a heart attack or stroke in the months after beginning treatment, a new study suggests. Within 6 months of a diagnosis, the risk of either event was more than twice that seen in people without cancer.
-
In Melanoma, Personalized Treatment Vaccines Show Promise
Results of an early-phase trial showed that a treatment vaccine personalized to a specific patient’s cancer generated a robust immune response against the cancer and may have helped to prevent it from returning.
-
Glioblastoma—Unraveling the Threads: A Q&A with Drs. Mark Gilbert and Terri Armstrong of the NIH Neuro-Oncology Branch
Progress against the brain cancer glioblastoma has been slow. Drs. Mark Gilbert and Terri Armstrong of NCI’s Neuro-Oncology Branch discuss why and what’s being done to change that.
-
Cancer Researchers Report Progress in Studying Exceptional Responders
Researchers who study exceptional responders—patients who have dramatic and long-lasting responses to treatments for cancer that were not effective for most similar patients—met recently to discuss the state of the science in this emerging field.
-
Extensive Lymph Node Surgery Does Not Increase Survival in Melanoma
A conservative approach to lymph node removal surgery may be best for people with melanoma that has spread from the skin to one or a small number of nearby lymph nodes, new results from a large international clinical trial suggest.
-
FDA Expands Approval of Ceritinib for ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
The FDA has approved the targeted therapy ceritinib as an initial treatment for patients with lung cancer that has a mutation in the ALK gene.
-
FDA Approves Pembrolizumab for Tumors with Specific Genetic Features
FDA approved pembrolizumab for patients with solid tumors that have specific genetic features, called mismatch repair deficiency and high microsatellite instability. This is the first approval based on a genetic feature, rather than cancer type.
-
Abiraterone Improves Survival for Some Men with Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer
In two large clinical trials, adding the hormone-blocking drug abiraterone to androgen-deprivation therapy (ADT) allowed men with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer to live longer than men who were treated with ADT alone.
-
Trastuzumab Emtansine Improves Survival in Previously Treated Metastatic HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
Two clinical trials show that trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) improves survival compared with other standard treatments for patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer that has progressed after treatment with other HER2-targeted drugs.
-
CAR T Cells: Expanding into Multiple Myeloma
Results from two early-phase trials presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting suggest that an immunotherapy using genetically engineered immune cells may be effective in patients with advanced multiple myeloma.
-
Less Chemotherapy May Be Best Choice for Some Patients with Colon Cancer, Study Shows
A shorter course of chemotherapy following surgery may be preferred to longer treatment for some patients with colon cancer, results of an international collaborative study suggest.
-
Patients Who Choose No Intervention for Small Thyroid Cancers Report Lack of Support
Patients who choose not to pursue immediate biopsy or treatment for small, asymptomatic thyroid cancers, or suspected cancers, can experience a lack of support from doctors and loved ones, a new study shows.